Growing Anomalies at the Large Hadron Collider Raise Hopes
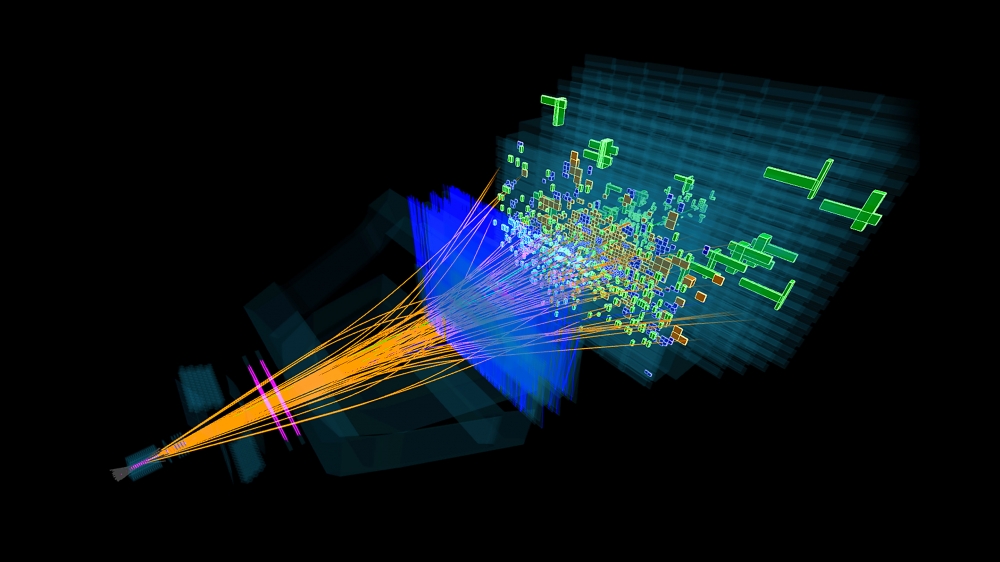
Computer reconstruction of a collision event in the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment. The collision produces a B meson, which subsequently decays into other particles that strike LHCb’s detectors. CERN/LHCb
Charlie Wood -- May 26, 2020
Amid the chaotic chains of events that ensue when protons smash together at the Large Hadron Collider in Europe, one particle has popped up that appears to go to pieces in a peculiar way.
All eyes are on the B meson, a yoked pair of quark particles. Having caught whiffs of unexpected B meson behavior before, researchers with the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment (LHCb) have spent years documenting rare collision events featuring the particles, in hopes of conclusively proving that some novel fundamental particle or effect is meddling with them.
In their latest analysis, first presented at a seminar in March, the LHCb physicists found that several measurements involving the decay of B mesons conflict slightly with the predictions of the Standard Model of particle physics — the reigning set of equations describing the subatomic world. Taken alone, each oddity looks like a statistical fluctuation, and they may all evaporate with additional data, as has happened before. But their collective drift suggests that the aberrations may be breadcrumbs leading beyond the Standard Model to a more complete theory.
“For the first time in certainly my working life, there are a confluence of different decays that are showing anomalies that match up,” said Mitesh Patel, a particle physicist at Imperial College London who is part of LHCb.
See full text